For IT Service companies looking for a technology platform to help them manage the service they provide to customers, like any change management or transformation project, it is advisable to understand where you are now and where you want to be in order to derive the best value from your investment.
What is the IT Service Management Maturity model?
This is the first step to understand where you are now as an organization in order to match your current and future needs, allowing the ITSM CRM you choose to grow with your business, releasing real business value and positive change from the beginning.
The maturity curve below is a summary view of how IT Service providers can start to benchmark themselves and plot their ITSM platform implementation phases as they move through the strategic steps – from a reactive cost center towards a value-add strategic service partner.
It’s an ongoing process of optimize and automate because of the changing business needs in a very rapidly changing market.
Whilst there has been much discussion and multiple formats of ITSM maturity models, the model proposed here is a simplified version – encompassing the stages, meanings and outcomes.
A word about ITIL and the ITSM maturity model
ITIL ((Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is part of a suite of 34 best-practice publications (ITIL 4) and provides guidance to service providers on the provision of quality IT services, and on the processes, functions and other capabilities needed to support them. Whilst ITIL is often mentioned as part of ITSM but it’s not mandatory to use the ITIL framework, however organizations are encouraged to adopt ITIL best practices and to adapt them to work in their specific environments to meet their needs (relevant to their stage on the maturity curve, resources and strategy), as it is the most widely recognized framework for IT Service Management in the world.
If we look at the IT Service Management maturity curve in model in terms of what operational activities and therefore functional requirements are relevant at each stage, this may help in terms of plotting your organization and your readiness at the appropriate maturity step.
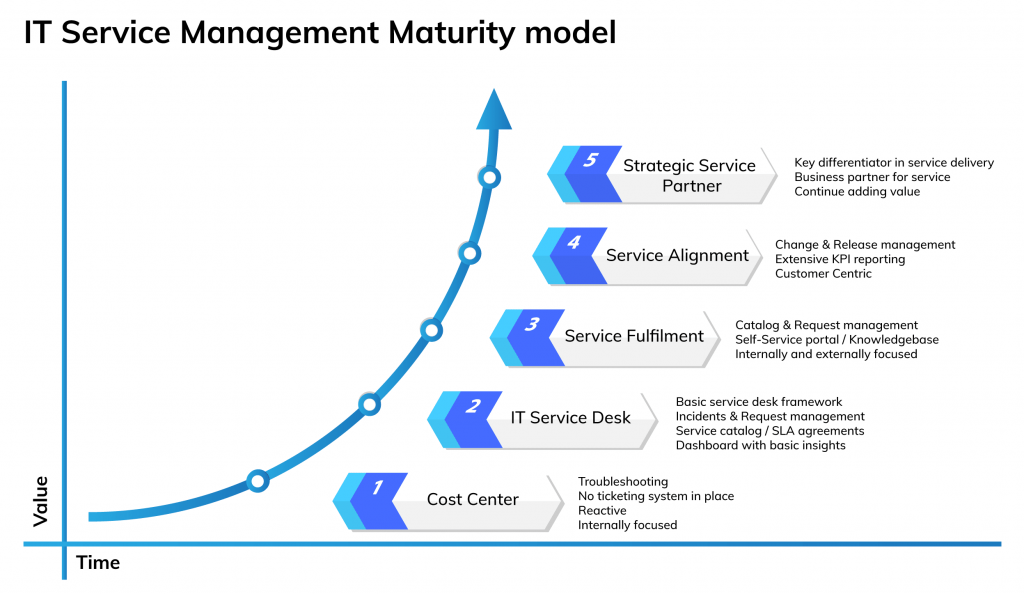
- Maturity Level 1: Cost Center – the various service departments in your organization operate in isolation and work independently to manage costs. These siloed departments use disparate service management tools, their processes are undocumented, ad hoc and disconnected. There are minimal IT operations, with tools confined to daily workplace apps. Optimizing service delivery to reduce unpredictability in these departments is not seen as essential and remains costly.
- Maturity Level 2: IT Service Desk – the service team provide on-demand support with a predominantly reactive nature. The service focus is on problem management processes with alert and event management features being requested. Customer inventory is starting to be measured due to costs and overheads. There is ambition to create and manage Service Level Agreements with customers, with the first steps to understand performance in incident management with basic dashboards. Although a basic Service Desk framework exists, there remains a degree of multiple service teams disconnected from each other with limited collaboration.
- Maturity Level 3: Service Fulfilment – the service function has moved to a proactive approach, with processes and guidelines in place across the business with appointed owners. Collaboration is increased with Knowledge Base features within a single service management solution. Performance and customer needs are being analyzed, trends spotted, and thresholds are being set in parallel with SLA management. The organization is able to predict problems in order to plan resource availability and has mastered its problem, change and asset management processes. The first steps are made toward a customer-centric approach with a self-service portal.
- Maturity Level 4: Service Alignment – the focus shifts from purely managing costs to customer-centric approaches across all service activities. The IT Service provider can guarantee SLAs with the support of extensive KPI reporting and capacity management. Change and release management processes are advanced and part of daily work.
- Maturity Level 5: Strategic Service Partner – IT service delivery becomes intrinsically linked with business strategies with added value demonstrated in real terms.
Article initially published on LinkedIn
by Jeroen Paters – Business Consultant at Prodware